Amazon
A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types Of Seller On Amazon
Fueled by innovative product ideas and a burning desire to succeed, you’ve set your sights on Amazon – the e-commerce giant. But before diving in, a crucial decision awaits: choosing the right seller account type. This decision hinges on factors like your sales volume, product nature, and business goals. Additionally, questions about Amazon FBA insurance and account investment requirements might be swirling in your mind.
Whether you’re a brick-and-mortar store venturing into the exciting world of e-commerce, an established brand seeking to expand your reach, or a wholesaler looking for a wider audience, Amazon offers a platform for you to thrive.
Different Types Of Sellers On Amazon
The world of Amazon can seem complex, especially for those venturing into selling. This guide breaks down the different types of sellers and fulfillment options available, empowering you to navigate the platform effectively.
1. 1P Amazon Sellers:
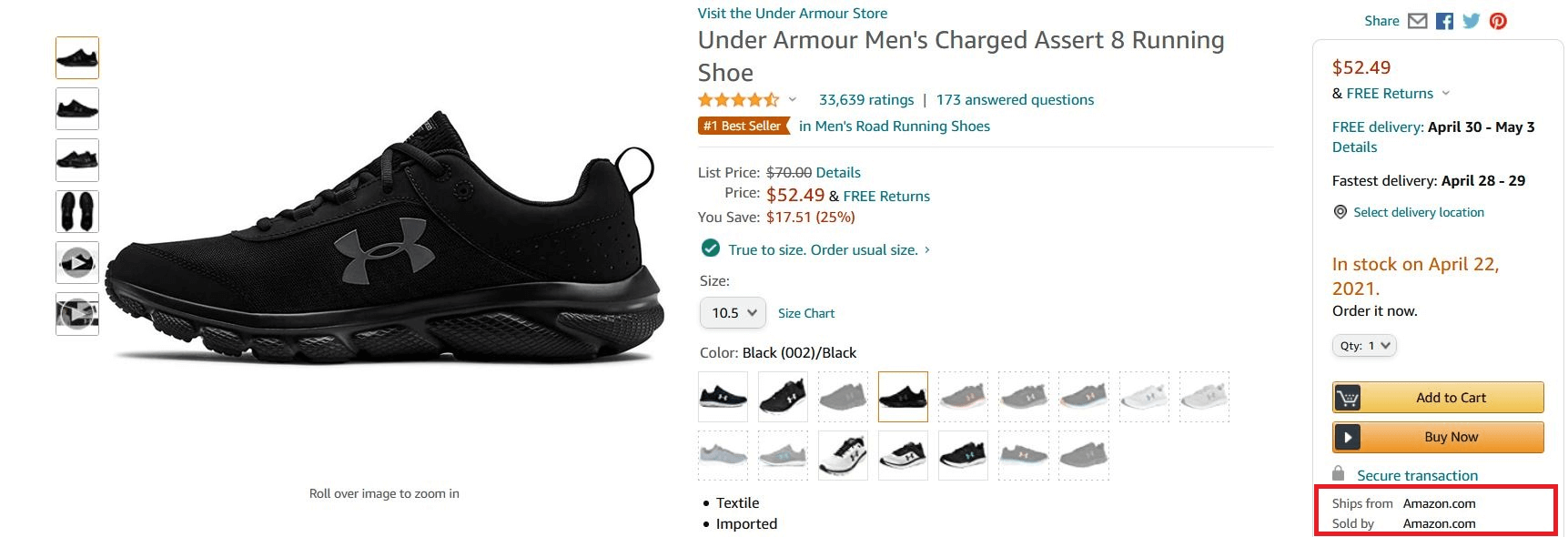
While Amazon is primarily a marketplace, it also acts as a seller itself (1P). It sells the brand’s products under its name like AmazonBasics or through wholesale partnerships. Unlike 3P sellers, Amazon itself manages inventory, fulfillment, and marketing for these product/brand owners. Dive deeper into the key differences between 1P and 3P sellers on Amazon here.
Instead of using Seller Central, 1P sellers (vendors who sell directly to Amazon) manage their business through Vendor Central. This dedicated platform streamlines communication and transactions between Amazon and its vendors. These are manufacturers or wholesalers who directly supply products to Amazon.
2. Third-Party (3P) Sellers:
Independent sellers on Amazon, known as Third-Party Sellers (3P sellers), leverage the giant’s extensive customer base to showcase and sell their products. When a 3P seller makes a sale, Amazon takes a commission, called a referral fee, for facilitating the transaction on it’s platform. This fee represents a small percentage of the selling price.
In essence, 3P sellers act like independent store owners within the larger Amazon marketplace. They are responsible for managing their inventory, creating product listings, setting prices, and fulfilling customer orders (often with the option to utilize Amazon’s fulfillment services). Third-party sellers have two categories, FBA and FBM, based on their order fulfillment practice.
3P sellers are further categorized into two groups based on fulfillment:
- Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA): This offers sellers to choose convenience. They send their products to Amazon’s warehouses where they are stored, packaged, and shipped to customers. FBA sellers enjoy benefits like streamlined logistics and Prime eligibility for their products, but incur additional fees for storage and fulfillment.
- Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM): Here, sellers manage the entire fulfillment process. They store their inventory, package orders, and ship them directly to customers. This approach offers greater control over shipping costs, but requires sellers to handle logistics independently.
3. Types Of Seller Accounts:
Understanding Seller Plans:
Amazon offers two seller plans on its Seller Central, each with different levels of perks:
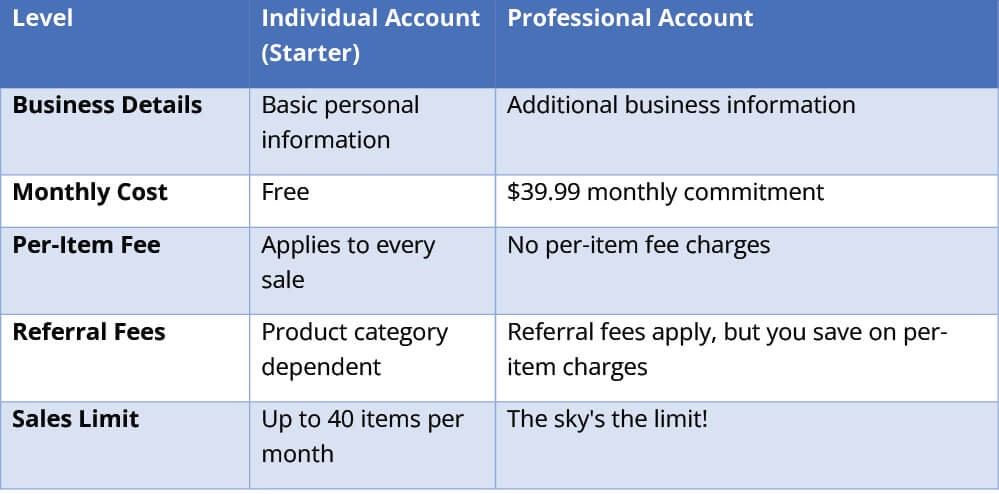
- Individual Seller Account: Ideal for low-volume sellers (less than 40 units per month). It has no monthly subscription fee but charges a per-item selling fee. However, exceeding 40 units in a month adds an additional fee, and individual sellers cannot compete for the coveted “Buy Box” placement.
- Professional Seller Account: Suited for higher-volume sellers (over 40 units per month). It comes with a monthly subscription fee but offers additional features like access to more product categories and the ability to compete for the Buy Box, which significantly increases product visibility.
4. Wholesale:
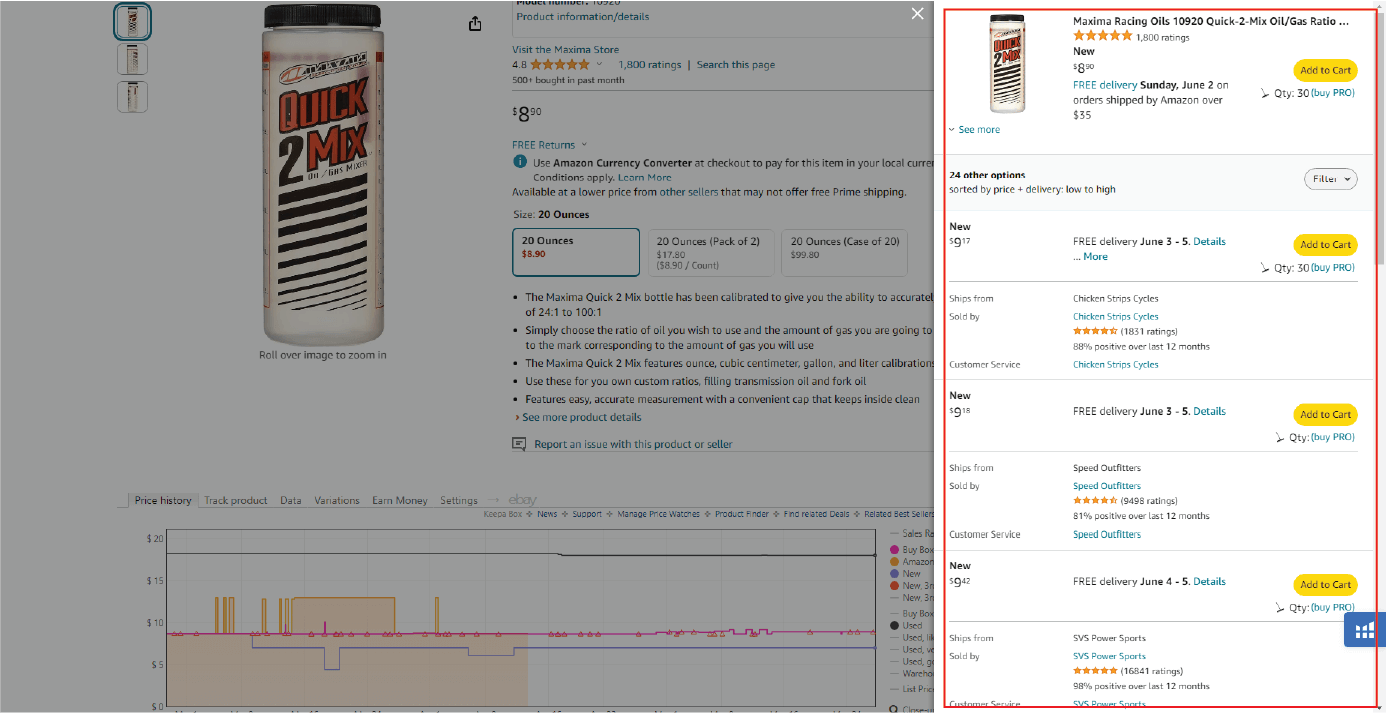
This time-tested approach involves purchasing products in bulk from distributors or manufacturers at a discounted price. As an Amazon wholesale seller, you’ll then resell these items individually on the platform, typically under the original brand name. While offering lower profit margins compared to other strategies, wholesaling requires minimal upfront investment in branding.
5. Arbitrage:
This strategy involves finding products at a lower price point elsewhere (online retailers, brick-and-mortar stores) and then reselling them on Amazon at a higher price to generate a profit. Unlike wholesale, arbitrage allows for more flexibility in sourcing inventory, as you’re not limited to bulk purchases. However, success hinges on identifying profitable opportunities and navigating potential pricing competition.
6. Private Label:
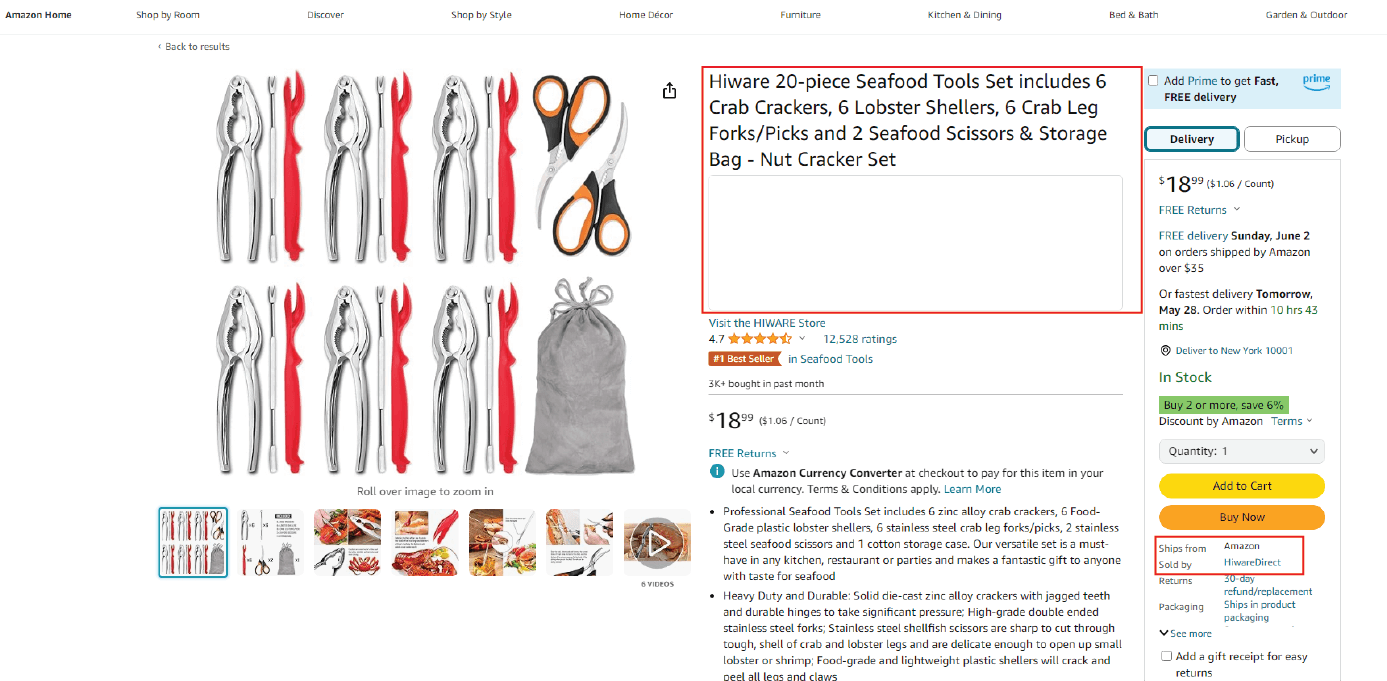
This approach empowers you to build your own brand. Private label sellers typically source or manufacture unique products (often from overseas suppliers) and then sell them under their own brand name on Amazon. This strategy allows for higher profit margins and greater control over branding and marketing. However, private label requires a more significant initial investment compared to other models.
7. Established Brands:
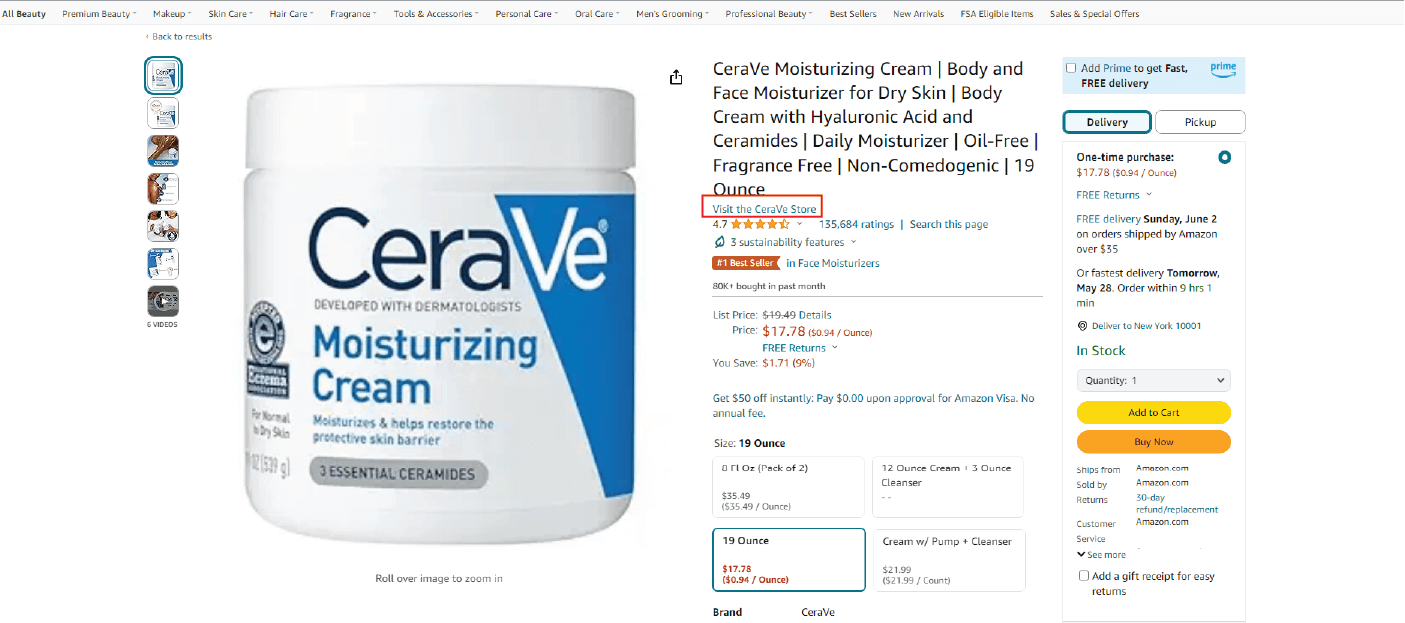
Many well-known brands leverage Amazon’s vast customer base to expand their reach. These brands typically utilize the Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) program, managing their own inventory and shipping logistics. By establishing a presence on Amazon, brands can tap into a wider audience and boost online sales without the additional costs of physical retail space.
Choosing the best strategy depends on your budget, risk tolerance, and business goals. Each approach offers unique advantages and drawbacks. Consider your resources and desired level of brand control when deciding which path best suits your needs.
How Third-Party Selling on Amazon Ensures E-commerce Success?
The allure of Amazon’s massive customer base is undeniable. But for aspiring sellers, navigating the platform’s options can be a head-scratcher. Deciding between the 1P (Amazon’s own sales) and 3P (third-party) model is a crucial first step. If you’re looking for control, flexibility, and the potential for higher profits, then 3P selling might be the golden ticket to your e-commerce success story. Here’s why:
1. Manage Your Brand’s Identity:
By partnering with a reliable 3P selling partner, you get to control your brand. You get to manage the brand’s identity across the marketplace with your 3P selling partner with compelling product listings, and competitive pricing. This builds brand loyalty and customer recognition, fostering a loyal following that transcends the Amazon marketplace, minus the hassle handled by the 3P seller.
2. Greater Inventory Control:
Unlike 1P sellers who work within Amazon’s purchasing framework, 3P sellers have complete control over the inventory. This means the 3P sellers can decide which products to stock, how much to stock, and adjust quantities based on demand. This flexibility ensures there is no dead stock left or scrambling to fulfill unexpected surges in orders.
3. Explore Profit Potential:
While Amazon takes a commission on each sale, 3P sellers have more freedom to set their own pricing. This allows you to factor in your costs and target a healthy profit margin. Additionally, you can leverage promotions and discounts to attract customers and boost sales.
4. Diversify Your Reach:
Amazon offers a global marketplace, but it’s not the only game in town. As a 3P seller, you can establish your ecommerce business on other channels like your own website or social media platforms. This multi-channel approach allows you to diversify your customer base and reduce dependence on a single platform.
5. Experimentation Playground:
The 3P model allows you to experiment and test the waters. You can start small with a limited product selection, gauge customer response, and refine your offerings based on market feedback. This iterative approach minimizes risk and helps you find a niche that resonates with your target audience.
6. Fulfillment Options:
3P sellers have a choice: leverage Amazon’s efficient Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program, or manage fulfillment independently (FBM). FBA offers convenience and fast shipping options, while FBM gives you more control over packaging and shipping costs. Choose the option that best suits your business needs and budget.
Conclusion:
The world of Amazon selling can be overwhelming, but the potential for sellers is huge. If you’re a brand operating in multiple marketplaces besides Amazon and wish to streamline your order fulfillment and maximize profits, then Multi-Channel Fulfillment by Amazon might be a suitable option for your brand. Learn more about MCF here.
Ready take over the marketplace with an immaculate brand presence? Prime Retail Solution can be your expert guide. We are a team of seasoned professionals dedicated to helping brands thrive in the Amazon marketplace. From listing optimization to fulfillment strategies, we offer a comprehensive suite of services to empower your brand and drive sales.
Contact Prime Retail Solution today for a FREE consultation and discover how we can help you turn your Amazon dream into a reality!
Share





